엑셀 VBA 강좌(8): 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본-자료형(Data type), 자료구조(Data structure)
이번 글은 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본 중 자료형(Data type)과 제공되는 자료구조(Data structure)에 대해 살펴본다.
이전 글에서 이어지는 내용이다.
엑셀 VBA 강좌(7): 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본-문법(Syntax)
3.3. 자료형
3.3.1. 기본 자료형
VB(또는 VBA)에서 지원하는 자료형을 요약하면 다음 표와 같다. 아래 출처의 표 내용중 Collection, Dictionary는 “자료 구조”에서 별도로 설명한다.
기본 자료형 목록
출처: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office/vba/language/reference/user-interface-help/data-type-summary
| 데이터 형식 | 저장 용량 | 범위 |
| Boolean | 2 bytes | True 또는 False |
| Byte | 1 byte | 0 ~ 255 |
| Collection | Unknown | Unknown |
| Currency (scaled integer) | 8 bytes | -922,337,203,685,477.5808 ~ 922,337,203,685,477.5807 |
| Date | 8 bytes | January 1, 100, to December 31, 9999 (100-01-01 ~ 9999-12-31) |
| Decimal | 14 bytes | +/-79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 with no decimal point +/-7.9228162514264337593543950335 with 28 places to the right of the decimal Smallest non-zero number is+/-0.0000000000000000000000000001 |
| Dictionary | Unknown | Unknown |
| Double (double-precision floating-point) | 8 bytes | -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 for positive values |
| Integer | 2 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| Long (Long integer) | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| LongLong (LongLong integer) | 8 bytes | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 Valid on 64-bit platforms only. |
| LongPtr (Long integer on 32-bit systems, LongLong integer on 64-bit systems) | 4 bytes on 32-bit systems 8 bytes on 64-bit systems | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 on 32-bit systems -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 on 64-bit systems |
| Object | 4 bytes | Any Object reference |
| Single (single-precision floating-point) | 4 bytes | -3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 for negative values 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values |
| String (variable-length) | 10 bytes + string length | 0 to approximately 2 billion |
| String (fixed-length) | Length of string | 1 to approximately 65,400 |
| Variant (with numbers) | 16 bytes | Any numeric value up to the range of a Double |
| Variant (with characters) | 22 bytes + string length (24 bytes on 64-bit systems) | Same range as for variable-length String |
| User-defined (using Type) | Number required by elements | The range of each element is the same as the range of its data type. |
이 중에서 가장 자주 사용하는 데이터 형식은 Int, Long, String, Boolean 정도이다.
Variant, User-defined 데이터 형식에 대해 아래에 추가로 설명한다.
Variant 데이터 형식
Variant 데이터 형식은 여러 데이터 형식을 저장하고 처리할 수 있는 특별한 데이터 형식이다. 변수를 선언할 때 데이터 형식을 생략하면 Variant 데이터 형식으로 지정된다. Variant 데이터 형식에 대한 자세한 내용은 아래 URL을 참고하기 바란다.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office/vba/language/reference/user-interface-help/variant-data-type
실행중에 Variant 변수가 어떤 데이터 형식을 저장하고 있는지 확인하려면 VarType 함수를 이용한다.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office/vba/language/reference/user-interface-help/vartype-function
구문
VarType(varname)
필수 요소인 varname 인수는 사용자 정의 형식의 변수를 제외한 변수가 들어 있는 Variant입니다.
반환형식
| 상수 | 값 | 설명 |
| vbEmpty | 0 | Empty(초기화되지 않음) |
| vbNull | 1 | Null(유효한 데이터 없음) |
| vbInteger | 2 | 정수 |
| vbLong | 3 | 긴 정수 |
| vbSingle | 4 | 단정도 부동 소수점 수 |
| vbDouble | 5 | 배정도 부동 소수점 수 |
| vbCurrency | 6 | 통화값 |
| vbDate | 7 | 날짜값 |
| vbString | 8 | 문자열 |
| vbObject | 9 | 개체 |
| vbError | 10 | 오류값 |
| vbBoolean | 11 | Boolean 값 |
| vbVariant | 12 | Variant(variant 배열에서만 사용) |
| vbDataObject | 13 | 데이터 액세스 개체 |
| vbDecimal | 14 | 십진값 |
| vbByte | 17 | 바이트값 |
| vbArray | 8192 | 배열 |
나는 개인적으로 Variant 데이터 형식을 잘 사용하지 않고 시트 데이터를 한번에 읽고 쓸 때에만 주로 사용한다. Variant arry를 이용하여 많은 양의 시트 데이터를 읽고 쓰는 방법에 대해서는 아래 글을 참고한다.
VBA 코딩 패턴: Range Loop-읽기(Read)
VBA 코딩 패턴: Range Loop-쓰기(Write)
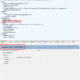
Variant 데이터 형식을 사용하는 예제 코드이다. 정수, 문자열, 실수, 날짜 데이터 형식을 모두 처리할 수 있는 것을 보여준다.
Sub VariantTest()
Dim a As Variant '데이터 형식을 생략하면 Variant 형식임
a = 1: Debug.Print a
a = "1": Debug.Print a
a = 1.1: Debug.Print a
a = CDate("2021-07-31"): Debug.Print a
End Sub
User-defined(사용자 정의) 데이터 형식
사용자 정의 자료형을 선언하고 사용할 수 있다. C언어의 ‘struct’와 비슷한 ‘Type’ keyword로 사용자 정의 자료형을 선언한다. User-defined 데이터 형식은 개체가 아니라서 선언하면 바로 instance가 생성되어 메모리가 할당되고 값을 입력할 수 있다.
User-defined 데이터 형식에 대한 자세한 내용은 아래 URL을 참고하기 바란다.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office/vba/language/how-to/user-defined-data-type
User-defined 데이터 형식의 예시 코드는 다음과 같다.
Type EmployeeRecord ' 사용자 정의 형식을 만듭니다.
ID As Integer ' 데이터 형식의 요소를 정의합니다.
Name As String
Address As String
Phone As Long
HireDate As Date
End Type
Sub CreateRecord()
Dim MyRecord As EmployeeRecord ' 변수를 선언합니다.
MyRecord.ID = 12003 ' 요소에 값을 할당합니다.
MyRecord.Name = "Andy"
MyRecord.HireDate = CDate("2021-07-31")
End Sub
3.3.2. 자료구조
자주 사용하는 자료구조는 Array, Collection, Dictionary가 있다. 각각에 대해 살펴보자.
Array
고정 개수의 Item을 가진다. 개체가 아니라서 선언하면 instance가 생성된다. 선언할 때 차원의 수와 각 차원의 하한, 상한 범위를 지정할 수도 있고, 실행시에 동적으로 배열의 차원, 범위를 변경할 수도 있다. 각 차원의 하한과 상한을 지정하지 않고 item의 개수만 지정할 경우 기본적으로 하한은 0이다. Option Base 1을 사용하면 기본 하한은 1이 된다.
선언 예시 코드
Dim DayArray(50) Dim Matrix(3, 4) As Integer Dim MyMatrix(1 To 5, 4 To 9, 3 To 5) As Double
각 차원 하한값/상한값 선언, 확인: LBound, UBound 사용
Dim A(1 To 100, 0 To 3, -3 To 4) LBound(A, 1) -> 1, UBound(A, 1) -> 100 ' 1차원 하한/상한 LBound(A, 2) -> 0, UBound(A, 2) -> 3 ' 2차원 하한/상한 LBound(A, 3) -> -3, UBound(A, 3) -> 4 ' 3차원 하한/상한
차원 크기 변경: Redim 문으로 동적 배열의 차원 크기를 변경한다.
Dim MyArray() As Integer ' 동적 배열을 선언합니다. Redim MyArray(5) ' 5개의 요소를 할당합니다. Redim Preserve MyArray(15) ' 15개의 요소로 크기를 변경합니다.
Item Loop(For Next)
'Split & Trim 처리
Public Function SplitTrim(aExpression As String, aDelimeter As String) As String()
Dim saOut() As String, i As Integer
saOut = Split(aExpression, aDelimeter)
For i = LBound(saOut) To UBound(saOut)
saOut(i) = Trim(saOut(i))
Next i
SplitTrim = saOut
End Function
초기화: Erase 문으로 배열 변수를 초기화한다.
' 배열 변수를 선언합니다.
Dim NumArray(10) As Integer ' 정수 배열입니다.
Dim StrVarArray(10) As String ' 변수 문자열 배열입니다.
Dim StrFixArray(10) As String * 10 ' 고정 문자열 배열입니다.
Dim VarArray(10) As Variant ' Variant 배열입니다.
Dim DynamicArray() As Integer ' 동적 배열입니다.
ReDim DynamicArray(10) ' 저장 공간을 할당합니다.
Erase NumArray ' 0으로 지정된 각 요소입니다.
Erase StrVarArray ' 길이가 0인 문자열 ("")로 지정된 각 요소입니다.
Erase StrFixArray ' 0으로 지정된 각 요소입니다.
Erase VarArray ' Empty로 지정된 각 요소입니다.
Erase DynamicArray ' 배열에 의해 사용되는 빈 메모리입니다.
Collection
Collection class는 동적 배열(Array)과 유사하다. 가변 갯수의 unique item을 Add, Remove할 수 있다. 개체이기 때문에 “Set” 과 “New”키워드를 이용하여 instance를 생성한다. Visual Basic 언어에서 개체에 reference를 생성하거나 새로운 reference를 할당할 때는 꼭 “Set” keyword를 사용해야 하고, 변수에 값을 할당할 때는 “Set” keyword가 필요없다. 개체를 다룰 때와 변수를 다룰 때를 잘 구분해야 문법 오류가 발생하지 않는다. 자주 실수할 수 있으니 주의가 필요하다.
Collection 개체 선언, instance 생성, Item 추가 등의 작업별 코드는 아래 표를 참고한다.
| Task | Sample Code |
| 선언 | Dim oCol As Collection |
| Instance 생성 | Set oCol = New Collection |
| 선언과 동시에 Instance 생성 | Dim oCol As New Collection |
| Item 추가 | oCol.Add “Apple” |
| Index로 Item 접근 | oCol(1) |
| Item 개수 | oCol.Count |
| Item Loop (For) | Dim l As Long For l = 1 to oCol.Count Debug.Print oCol(l) Next |
| Item Loop (For Each) | Dim fruit As Variant For Each fruit in oCol Debug.Print fruit Next |
| Item 제거 (Index 지정) | oCol.Remove(1) |
| Instance 제거 | Set oCol = Nothing |
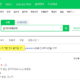
Collection 을 사용하는 예시 코드는 다음과 같다. 참고로 Collection의 Item은 1부터 시작한다.
Sub CollectionTest()
Dim oCol As Collection
Set oCol = New Collection
oCol.Add "Apple"
oCol.Add "Strawberry"
oCol.Add "Lemon"
oCol.Add "Banana"
Debug.Print oCol(1)
Debug.Print oCol.Item(1)
Debug.Print "----------"
Dim l As Long
For l = 1 To oCol.Count
Debug.Print oCol(l)
Next
Debug.Print "----------"
oCol.Remove (1)
Dim fruit As Variant
For Each fruit In oCol
Debug.Print fruit
Next
Set oCol = Nothing
End Sub
'출력
Apple
Apple
----------
Apple
Strawberry
Lemon
Banana
----------
Strawberry
Lemon
Banana
Dictionary
Key-Value 구조의 가변 unique Item을 관리할 수 있고, item을 동적으로 Add/Remove 할 수 있다.
Python 언어의 Dictionary, C++의 HashMap, Java의 HashMap과 유사한 자료구조이다. Key값으로 접근할 때 성능은 O(1) 수준이다.
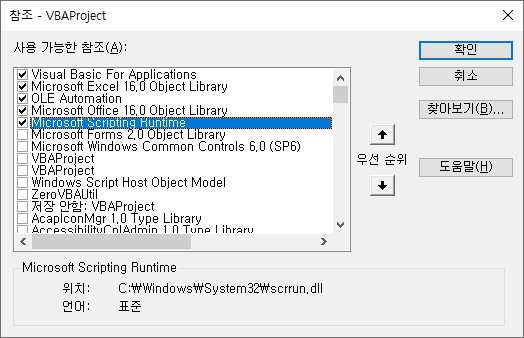
Dictionary class는 기본으로 제공되지 않는다. Early binding 방식으로 사용하려면 먼저 “Microsoft Scripting Runtime”을 참조해야 한다. Late binding 방식으로 사용하려면 CreateObject를 통해 instance를 생성하고 사용한다.
Dictionary 개체 선언, instance 생성, Item 추가 등의 작업별 코드는 아래 표를 참고한다.
| Task | Sample Code |
| 선언 (early binding) | Dim oDic As Dictionary |
| Instance 생성 (early binding) | Set oDic = New Dictionary |
| 선언 (late binding) | Dim oDic As Object |
| Instance 생성 (late binding) | Set oDic = CreateObject(“Scripting.Dictionary”) |
| Item 추가 | oDic.Add “Apples”, 50 |
| Value 변경 | oDic(“Apples”) = 60 |
| Value 얻기 | appleCount = oDic(“Apples”) |
| Key가 존재하는지 확인 | oDic.Exists(“Apples”) |
| Item 삭제 | oDic.Remove(“Apples”) |
| 모든 Item 삭제 | oDic.RemoveAll |
| Item 개수 | oDic.Count |
| Item Loop (For Each) | Dim key As Variant For Each key in oDic.Keys Debug.Print key, oDic(key) Next key |
| Item Loop (For, Early binding only) | Dim l As Long For l = 0 To oDic.Count -1 Debug.Print oDic.Keys(l), oDic.Items(l) Next l |
Dictionary를 사용하는 예시 코드는 다음과 같다. 참고로 Dictionary의 Items는 0부터 시작한다.
Sub DictionaryTest()
Dim oDic As Dictionary
Set oDic = New Dictionary
oDic.Add "A", "Apple"
oDic.Add "S", "Strawberry"
oDic.Add "L", "Lemon"
oDic.Add "B", "Banana"
Debug.Print oDic("A")
Debug.Print oDic.Items(0)
Debug.Print "----------"
Dim l As Long
For l = 0 To oDic.Count - 1
Debug.Print oDic.Items(l)
Next
Debug.Print "----------"
oDic.Remove ("A")
Dim key As Variant, fruit As String
For Each key In oDic.Keys
fruit = oDic(key)
Debug.Print fruit
Next
Set oDic = Nothing
End Sub
'출력
Apple
Apple
----------
Apple
Strawberry
Lemon
Banana
----------
Strawberry
Lemon
Banana
Dictionary 개체를 For Loop 구문으로 탐색할 때 key값을 담을 변수는 Variant 또는 Object 형식만 가능하다. 위 예시에서 23, 24 행의 코드에서는 Variant 형식을 사용했다.
이번 글에서는 VBA 데이터 형식과 자료구조에 대해 살펴보았다. 특히 Collection과 Dictionary는 자주 사용할 가능성이 매우 높기 때문에, 잘 익혀 두기 바란다. 다음에는 VBA 코딩시 알아두면 좋은 How-To에 대해 살펴보겠다.
<< 관련 글 목록 >>
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌를 시작합니다. (강좌예고, feat.엑셀 VBA를 권장하는 이유)
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(1): 엑셀 VBA 개요
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(2): 엑셀 VBA 기초
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(3): 엑셀 Object Model
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(4): 엑셀 Object Model 다루기
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(5): 엑셀 파일 확장자, VBE, 글꼴 설정
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(6): 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본-변수
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(7): 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본-문법(Syntax)
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(8): 엑셀 VBA 언어 기본-자료형(Data type), 자료구조(Data structure)
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(9): 엑셀 VBA How-To
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌(10): 엑셀 VBA로 개발하여 사용중인 도구
- 엑셀 VBA 강좌 전체 목차