Data standard inspection tool_2.3. Data standard dictionary composition
This is a continuation of the previous article. Let's take a look at the data standard dictionary configuration.
Data standard inspection tool_2.1. Screen composition, 2.2. Standard inspection function
2.3. Data standards preconfigured
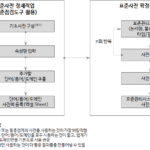
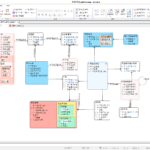
The data standard dictionary is the input and standard for standard inspection. A standard dictionary consists of three categories: standard words, standard terms, and standard domains. Examine each component of the standard dictionary and its relationship.
2.3.1. Data standard preconfiguration overview
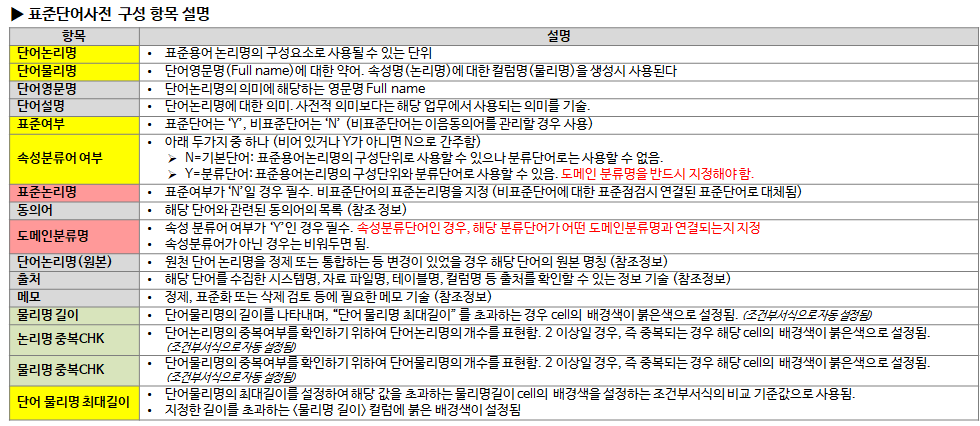
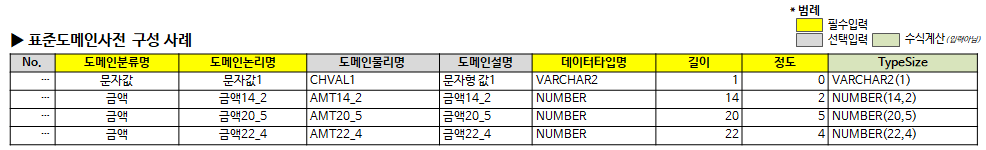
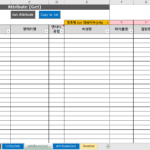
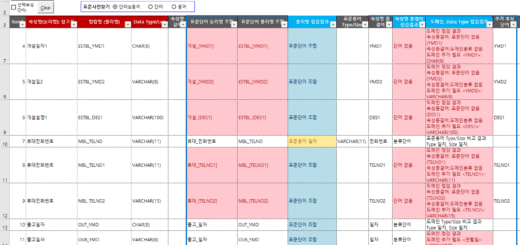
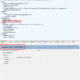
The dictionary of standard words, terms, and domains consists of the following items. Column titles with yellow background are required input, gray background is optional input, red background is conditional required input, green background is automatically calculated by formula, and some (length, duplicate CHK, etc.) are background color by conditional formatting is set
The following points are key here:
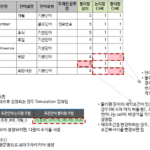
▼ Relationship between standard word dictionary and standard domain dictionary
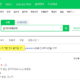
- The domain classification name of the standard word dictionary is linked to the domain classification name of the standard domain dictionary. Only the standard words whose attribute classifier is “Y” are applicable.
- For example, in the image above, the word “amount” is the attribute classifier “Y”, the domain classification name is “amount”, and there are 3 domains (amount 14_2, amount 20_5, amount 22_4) that can be used in the linked standard domain dictionary. .
▼ Relationship between the standard terminology dictionary and the standard domain dictionary
- The domain logical name of the standard term dictionary is connected to the domain logical name of the standard domain dictionary.
- All standard terms must specify a domain logical name, and the domain logical name must be defined in the standard domain dictionary.
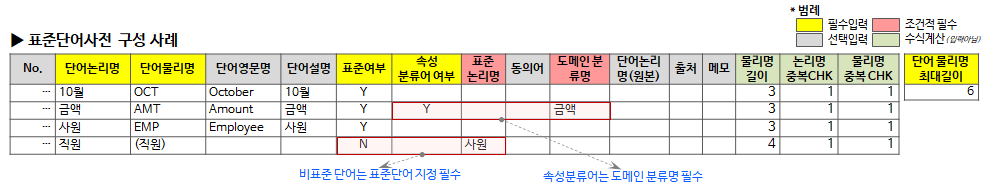
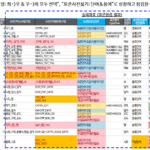
2.3.2. Standard word dictionary configuration example and item description
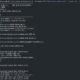
The standard word dictionary is composed as follows.
A description of each item is as follows.
- Word Logical Name: A unit that can be used as a component of a standard term logical name
- Word physical name: Abbreviation for the full name of the word. Used when creating column names (physical names) for attribute names (logical names).
- English word name: English name corresponding to the meaning of the word logical name Full name
- Word Description: The meaning of the word logic name. Describe the meaning used in the work rather than the dictionary meaning.
- Standard: 'Y' for standard words, 'N' for non-standard words (non-standard words are used when managing allophone synonyms)
- Attribute Classifier: One of the following two (if it is empty or not Y, it is regarded as N)
- N=Basic word: Can be used as a structural unit of a standard term or logical name, but cannot be used as a classification word.
- Y = Classification word: Can be used as a structural unit and classification word for standard terms and logical names. A domain classification name must be specified.
- Standard logic name: Required if standardization is 'N'. Specify the standard logic name of the non-standard word (replaced with the standard word connected when checking the standard for the non-standard word)
- Synonyms: A list of synonyms related to the word (reference information)
- Domain Classification Name: Required if attribute classifier is 'Y'. In the case of an attribute classification word, specify which domain classification name the corresponding classification word is connected to. Leave blank if it is not an attribute classifier.
- Logical word name (original): Original name of the word in case there is a change such as refining or integrating the original word logical name (reference information)
- Source: Information technology that can verify the source, such as the name of the system that collected the word, the name of the data file, the name of the table, and the name of the column (reference information)
- Memo: memo description required for refinement, standardization or deletion review (reference information)
- Length of physical name: Indicates the length of the physical name of the word. If it exceeds the “maximum length of the physical name of a word,” the background color of the cell is set to red. (automatically set as conditional formatting)
- Duplicate logical name CHK: Expresses the number of logical word names to check whether logical word names are duplicated. If it is 2 or more, that is, if it is overlapping, the background color of the corresponding cell is set to red. (automatically set as conditional formatting)
- Duplicate physical name CHK: Expresses the number of physical word names to check whether physical word names are duplicated. If it is 2 or more, that is, if it is overlapping, the background color of the corresponding cell is set to red. (automatically set as conditional formatting)
- Maximum length of word physical name: Used as a reference value for comparison of conditional formatting that sets the maximum length of physical word name and sets the background color of the cell with the length of the physical name exceeding the value. A red background color is set for the <physical name length> column that exceeds the specified length.
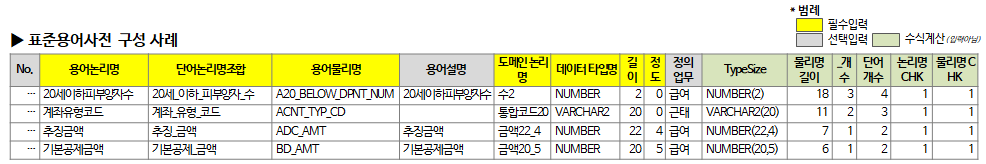
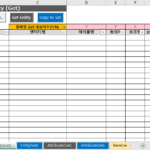
2.3.3. Examples of standard terminology dictionary composition and item description
The standard terminology dictionary is composed as follows.
A description of each item is as follows.
- Term logic name: A unit that is composed of standard words and can be used as an attribute logic name
- Word logical name combination: standard word logical name combination constituting a term logical name (connecting logical word names with an underscore (_) character)
- Terminological name: Combination of standard word physical names (abbreviations) constituting terminological names (connecting physical names of words with underscore (_) characters)
- Terminology: The meaning of the term logic name. The meaning used in the relevant business should be described rather than the dictionary meaning, but if the term logic name itself can explain the meaning in detail, it is okay to use the term logic name at least.
- Domain Logical Name: The logical name of the domain assigned to the term
- Datatype name: The name of the datatype of the domain specified in the term (eg NUMBER, VARCHAR2, etc.). It can be used as a logical data type, but the physical data type is currently recommended.
- Length: The data length of the domain specified in the term. Length in case of string type, Precision in case of number type, 0 if length designation is not required such as BLOB/DATE
- Degree: The degree of data in the domain specified in the term. It has meaning only for numeric types, and describes 0 for other types.
- Justice task: The name of the task that uses the term when initially registering the term (to confirm the source task of the term)
- TypeSize: A concatenated value of data type name, length, and degree
- Physical Name Length: Indicates the length of the term physical name
- _count: The number of underscore(_) included in the term physical name (one less than the number of words)
- Number of words: The number of words constituting the terminological name. Used to check if it consists of too many words (e.g. 6 or more)
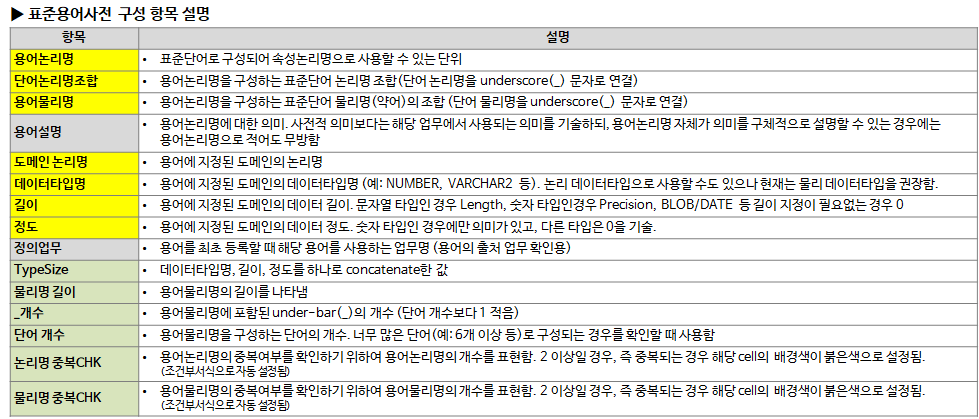
- Logical Name Duplication CHK: Expresses the number of logical term names to check whether the term logical names are duplicated. If it is 2 or more, that is, if it is overlapping, the background color of the corresponding cell is set to red. (automatically set as conditional formatting)
- Duplicate physical name CHK: Expresses the number of physical term names to check whether physical term names are duplicated. If it is 2 or more, that is, if it is overlapping, the background color of the corresponding cell is set to red. (automatically set as conditional formatting)
2.3.4. Examples of standard domain dictionary configuration and description of items
The standard domain dictionary is configured as follows.
A description of each item is as follows.
- Domain classification name: A clear guideline for classification by grouping individual domains. Assigned and connected to the classification word of the attribute.
- Domain Logical Name: The logical name of the domain. It is not a name that is used directly, but it is defined in a meaningful and non-redundant way.
- Domain Physical Name: The physical name of the domain. It is not a name that is used directly, but it is defined in a meaningful and non-redundant way.
- Domain Description: Description of the specifics of the domain
- Data type name: The name of the data type of the domain (eg NUMBER, VARCHAR2, etc.). It can be used as a logical data type, but the physical data type is currently recommended.
- Length: The data length of the domain. Length in case of string type, Precision in case of number type, 0 if length designation is not required such as BLOB/DATE
- Extent: The degree of data in the domain. It has meaning only for numeric types, and describes 0 for other types.
- TypeSize: A concatenated value of data type name, length, and degree
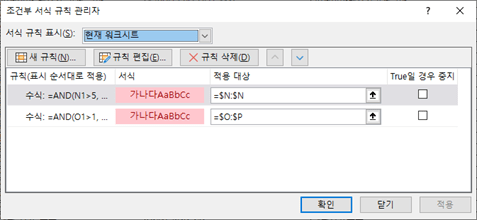
2.3.5. Note: Conditional formatting of standard dictionary sheets
The background color and font color of each cell in each sheet are set using conditional formatting. (Excluding the standard domain dictionary) If you want to change the color settings, change the rules, formats, and application targets in conditional formatting and apply them.
In the attribute standard inspection sheet, conditional formatting is used to automatically set the font color or background color according to the inspection result. The orange or red series means the object to be supplemented, and the blue series means the reference information.
In the standard word dictionary sheet, conditional formatting is used to set the background color when the length of the physical name exceeds the designated maximum length or when the logical name of a word overlaps.
In the standard glossary sheet, conditional formatting is used to set the background color when the number of word combinations of a term exceeds 5 or when the logical name of a term is duplicated.
So far, we have looked at the functions of the standard inspection tool and the composition of the standard dictionary. Next, we will look at an example of a standard check result.
<< List of related articles >>
- Data standard inspection tool_1.Overview
- Data standard inspection tool_2.1. Screen composition, 2.2. Standard inspection function
- Data standard inspection tool_2.3. Data standard dictionary composition
- Data Standard Check Tool_3. Standard Check Case Results
- Data standard check tool_4.Attachment
- How to Fix Data Standard Check Tool_v1.33 Error “Not enough memory”
- Data Standard Check Tool Description Contents , Download