Excel VBA Course (3): Excel Object Model
2.3. Excel Object Model
Excel VBA is a programming language that deals with Excel. More precisely, it is a language that handles Excel's Object Model. You need to know how Excel is structured to be able to handle it well.
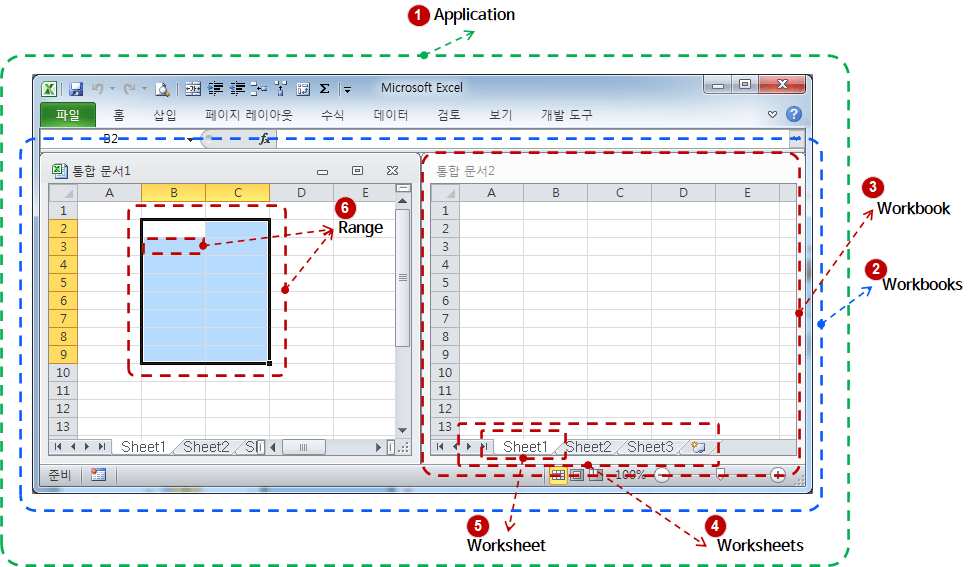
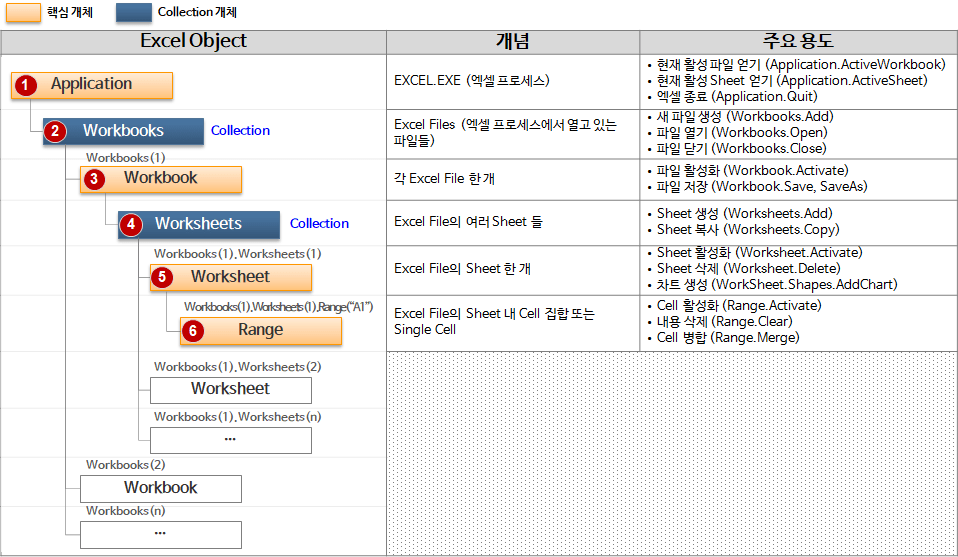
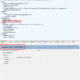
If you understand just one picture below, you can understand all the most important and frequently used concepts in the Excel Object Model.
The Excel in the figure above is the 2010 version. I think it is more suitable for understanding the Excel Object Model concept, so I explain it with the Excel 2010 version. Regardless of the version of Excel, the Object Model concept is the same.
This single figure contains all the essential concepts of the Excel Object Model. Let's look at the concept and details of each object.
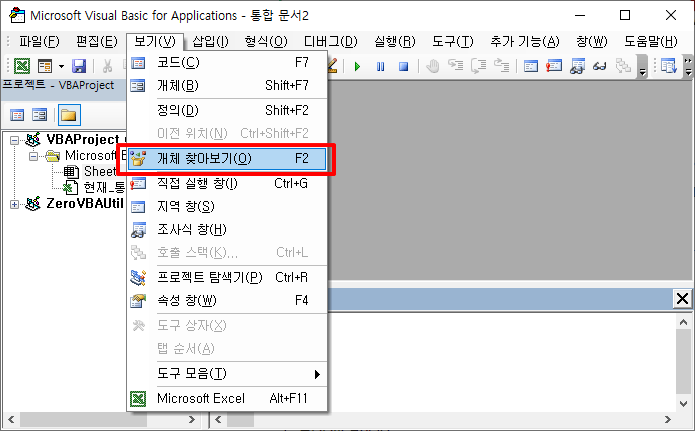
For reference, if you execute “View > Browse Objects” in the VBA editor, you can check the detailed properties, functions, procedures (subs), and events of each object.
(The VBA editor can be accessed by clicking the “Visual Basic” button on the developer tool ribbon menu, or by using a shortcut key.) Alt + F11 appears when you press .)
2.3.1. Application
Application refers to the Excel process. Use the Application object to control or terminate the running Excel.
More information on the Application object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Application object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Application object is as follows.
'Application 사용 코드 #1: 파일 활성화 하기
Application.Windows("book1.xls").Activate
'Application 사용 코드 #2: 엑셀 종료하기
Application.Quit()
2.3.2. Workbooks
Manages a collection of files open in a single Excel process. It is used for purposes such as creating a new file, opening or closing a file. When accessing a specific file from the file list, Workbooks(1), Workbooks(2), … , can be accessed with Workbooks(n).
More information on the Workbooks object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Workbooks object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Workbooks object is as follows.
'Workbooks 사용 코드 #1: 모든 파일 닫기 Workbooks.Close 'Workbooks 사용 코드 #2: 새로운 파일 생성하기 Workbooks.Add 'Workbooks 사용 코드 #3: 파일 열기 Workbooks.Open FileName:="File.xlsx", ReadOnly:=True
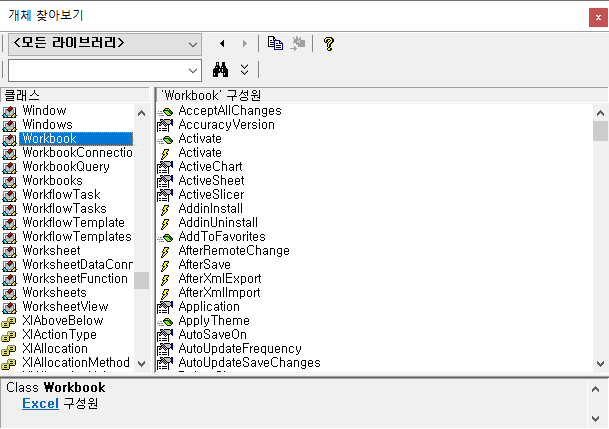
2.3.3. Workbook
Indicates one specific file among the list of files open in one Excel process. Used for closing or saving files.
More information on the Workbook object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Workbook object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Workbook object is as follows.
'Workbook 사용 코드 #1: 파일 닫기 Workbook.Close 'Workbooks 사용 코드 #2: 저장하기 Workbook.Save 'Workbooks 사용 코드 #3: 다른 이름으로 저장하기 Workbook.SaveAs Filename:="NewFile.xlsx"
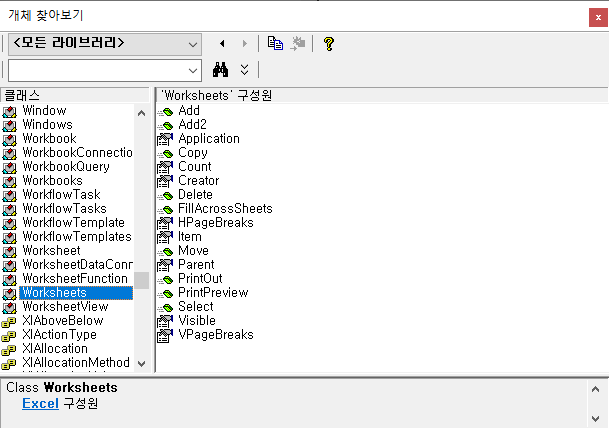
2.3.4. Worksheets
Manages a collection of sheets in a file. It is used for purposes such as creating or deleting a new sheet.
More information on the Worksheets object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Worksheets object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Worksheets object is as follows.
'Worksheets 사용 코드 #1: 첫번째 시트 앞에 2개 시트 추가
Worksheets.Add Count:=2, Before:=Sheets(1)
'Worksheets 사용 코드 #2: 시트 개수 출력
Debug.Print Worksheets.Count
'Worksheets 사용 코드 #3: Sheet3 뒤에 Sheet1 복사
Worksheets("Sheet1").Copy After:=Worksheets("Sheet3")
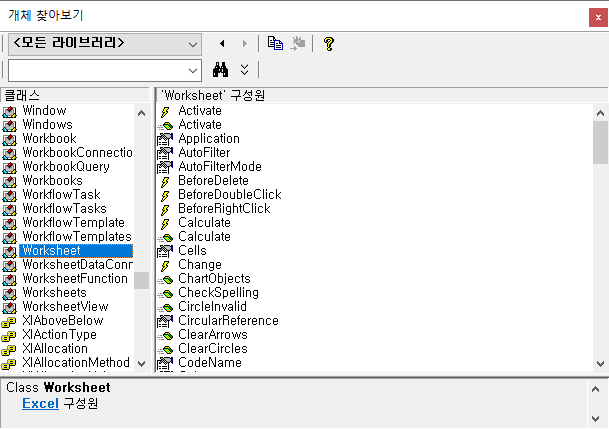
2.3.5. Worksheet
Points to a single sheet within a file. Used for activating, deleting, hiding, or showing sheets.
More information on the Worksheet object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Worksheet object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Worksheet object is as follows.
'Worksheet 사용 코드 #1: 시트 활성화
Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate
'Worksheet 사용 코드 #2: 시트 삭제
Worksheets("Sheet1").Delete
'Worksheet 사용 코드 #3: 시트 숨기기
Worksheets(1).Visible = False
'Worksheet 사용 코드 #4: 시트 보이기
Worksheets(1).Visible = True
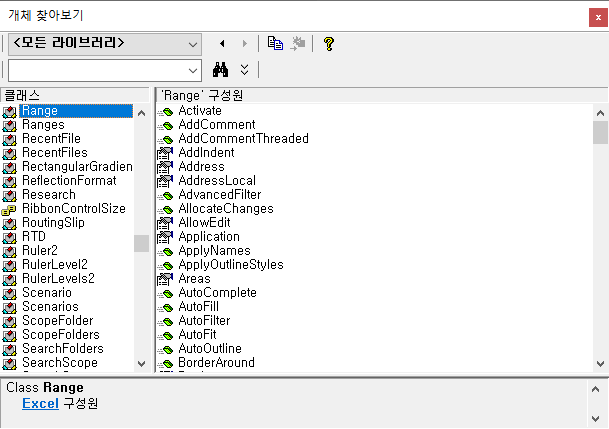
2.3.6. Range
It refers to one cell or several cells in one sheet. It is used to enter a value in a cell, delete it, or merge cells. It is the most used object when coding with Excel VBA.
More information about the Range object can be found in the Microsoft article below.
Range object (Excel) | Microsoft Docs
Example code using the Range object is as follows:
'Range 사용 코드 #1: A1 cell의 값을 A5에 입력
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A5").Value = _
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Value
'Range 사용 코드 #2: A1:E10 영역의 내용 삭제
Worksheets(1).Range("A1:E10").ClearContents
'Range 사용 코드 #3: A2(2행, 1열)에 B1:B5 합계 수식 입력
Worksheets(1).Range("A2").Formula = "=Sum(B1:B5)"
Worksheets(1).Cells(2, 1).Formula = "=Sum(B1:B5)"
'Range 사용 코드 #4: 5행 삭제하기
Worksheets(1).Rows(5).Delete
'Range 사용 코드 #5: 3열(C) 삭제하기
Worksheets(1).Columns("C").Delete
Worksheets(1).Columns(3).Delete
'Range 사용 코드 #6: A1:A2 cell 병합
Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A2").Merge
A brief summary of the hierarchical structure, concept, and purpose of the Excel Object Model examined so far is as follows.
Above, we briefly looked at the Excel Object Model. If you take a closer look with the object search function, you can see that all functions, properties, and events of Excel that can be executed with the mouse and keyboard are provided as an object model. Therefore, you must have a good understanding of Excel functions and use them well to make good use of the Excel Object Model. This means that you can use Excel VBA as much as you use Excel.
Next, we will look at example codes that use objects of the Excel Object Model, and explain the Excel Object Model in more detail.
<< Related article list >>
- Start the Excel VBA course. (Lecture notice, feat. Why we recommend Excel VBA)
- Excel VBA Course(1): Overview of Excel VBA
- Excel VBA Course (2): Excel VBA Basics
- Excel VBA Course (3): Excel Object Model
- Excel VBA Course (4): Working with Excel Object Model
- Excel VBA Course (5): Excel File Extension, VBE, Font Settings
- Excel VBA Course (6): Excel VBA Language Basics - Variables
- Excel VBA Course (7): Excel VBA Language Basics - Syntax
- Excel VBA Course (8): Excel VBA Language Basics - Data Types, Data Structures
- Excel VBA Courses (9): Excel VBA How-To
- Excel VBA Course (10): Tools developed and used with Excel VBA
- Full Table of Contents for Excel VBA Courses