Oracle Character Set Conversion (5): 5. Oracle Recommended Practice
Let's look at Oracle's recommended character set conversion method. You can check CSALTER usage method and limitations, CSSCAN usage method and execution order, execution result file, and DDL that creates CSSCAN execution result storage table.
This is a continuation of the previous article.
Oracle Character Set Conversion (4): 4.Configuring the Test Environment
5. Oracle Recommended Character Set Conversion Method (CSALTER, CSSCAN)
Oracle recommends using the Full Export & Import method and the CSALTER script. First, let's look at how to use CSALTER.
5.1. How to use CSALTER
Oracle documentation can be found at the URL below.
Execute the following procedure to change the character set of the database.
- Shut down the database, using either a SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE or a SHUTDOWN NORMAL statement.
- Do a full backup of the database, because the CSALTER script cannot be rolled back.
- Start up the database.
- Run the Database Character Set Scanner utility.
CSSCAN /AS SYSDBA FULL=Y… - Run the CSALTER script.
@@CSALTER.PLB
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; — or SHUTDOWN NORMAL;
STARTUP;
However, CSALTER does not convert user-generated data. (Some excerpts from the above URL's document content)
Note that the CSALTER script does not perform any user data conversion. It only changes the character set metadata in the data dictionary. Thus, after the CSALTER operation, Oracle behaves as if the database was created using the new character set.
This is a limitation of CSALTER, and using CSALTER for character set conversion is not suitable for most application environments.
However, CSSCAN (Database Character Set Scanner utility) is suitable for the purpose of identifying in advance the data that can be converted and the data that is problematic during conversion for the database to be converted.
5.2. How to use CSSCAN
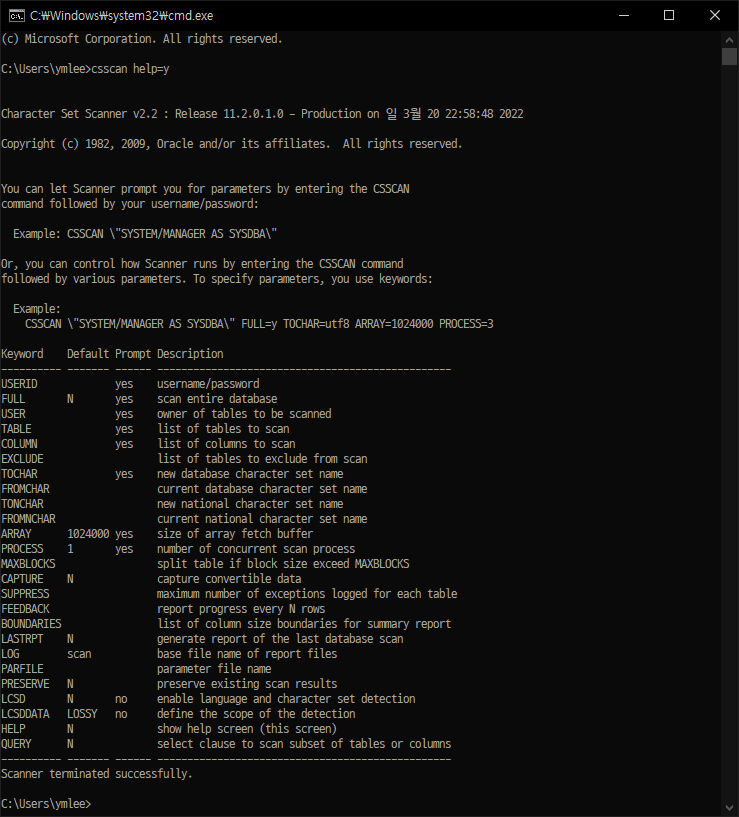
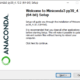
You can check the parameters required to run csscan with the following command.
csscan help=y
C:\Users\ymlee>csscan help=y
Character Set Scanner v2.2 : Release 11.2.0.1.0 - Production on 일 3월 20 22:58:48 2022
Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
You can let Scanner prompt you for parameters by entering the CSSCAN
command followed by your username/password:
Example: CSSCAN \"SYSTEM/MANAGER AS SYSDBA\"
Or, you can control how Scanner runs by entering the CSSCAN command
followed by various parameters. To specify parameters, you use keywords:
Example:
CSSCAN \"SYSTEM/MANAGER AS SYSDBA\" FULL=y TOCHAR=utf8 ARRAY=1024000 PROCESS=3
Keyword Default Prompt Description
---------- ------- ------ -------------------------------------------------
USERID yes username/password
FULL N yes scan entire database
USER yes owner of tables to be scanned
TABLE yes list of tables to scan
COLUMN yes list of columns to scan
EXCLUDE list of tables to exclude from scan
TOCHAR yes new database character set name
FROMCHAR current database character set name
TONCHAR new national character set name
FROMNCHAR current national character set name
ARRAY 1024000 yes size of array fetch buffer
PROCESS 1 yes number of concurrent scan process
MAXBLOCKS split table if block size exceed MAXBLOCKS
CAPTURE N capture convertible data
SUPPRESS maximum number of exceptions logged for each table
FEEDBACK report progress every N rows
BOUNDARIES list of column size boundaries for summary report
LASTRPT N generate report of the last database scan
LOG scan base file name of report files
PARFILE parameter file name
PRESERVE N preserve existing scan results
LCSD N no enable language and character set detection
LCSDDATA LOSSY no define the scope of the detection
HELP N show help screen (this screen)
QUERY N select clause to scan subset of tables or columns
---------- ------- ------ -------------------------------------------------
Scanner terminated successfully.
For detailed description of each parameter, refer to the following URL.
csscan is executed in the following order.
- Create schema: $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/csminst.sql Execute
- Create directory: Create D:\temp\csscan (for saving execution result file)
- run csscan
- Check the csscan execution result
Three files are created as a result of csscan execution.
- scan.txt: scan result summary report
- scan.out: scan target table information
- scan.err: error details
scan.txt (scan result summary report) consists of the following contents. (Click to go to oracle documentation)
- Database Size
- Database Scan Parameters
- Scan Summary
- Data Dictionary Conversion Summary
- Application Data Conversion Summary
- Application Data Conversion Summary Per Column Size Boundary: Output only when BOUNDARIES parameter is specified
- Distribution of Convertible Data Per Table
- Distribution of Convertible Data Per Column
- Indexes To Be Rebuilt
- Truncation Due To Character Semantics
Changeless, Convertible, Truncation, and Lossy in [Data Conversion Summary] can be found in the document below.
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/server.112/e10729/ch12scanner.htm#g1019330
| Status | Description |
| changeless | Data remains the same in the new character set – No data change during character set conversion |
| Convertible | Data can be successfully converted to the new character set – Data can be changed during character set conversion |
| Truncation | Data will be truncated if conversion takes place – Data is truncated when converting character set |
| Lossy | Character data will be lost if conversion takes place – Data loss (broken) when converting character set |
5.2.1. Table to save CSSCAN execution results
The csscan result is stored in the table below among several tables created when csminst.sql is executed.
- CSM$TABLES
- CSM$COLUMNS
- CSM$ERRORS
The point to note is that every time CSSCAN is executed, all data in this table is initialized. (scan.txt, scan.out, and scan.err files are also initialized)
If you want to compare the results while executing CSSCAN several times, it is better to back it up in a separate table.
Please refer to the DDL below for backup.
CREATE TABLE Z_CSSCAN_COL_SUMMARY
AS
SELECT '20140507' BASE_DT, U.USERNAME, TC.TABLE_NAME, TC.COLUMN_NAME
,CC.NUMROWS, CC.NULCNT, CC.CNVCNT, CC.CNVTYPE, CC.ERRCNT, CC.SIZERR
,CC.CNVERR, CC.MAXSIZ, CC.CHRSIZ
FROM CSMIG.CSM$COLUMNS CC INNER JOIN DBA_USERS U
ON (CC.USR# = U.USER_ID)
INNER JOIN DBA_OBJECTS O
ON (CC.OBJ# = O.OBJECT_ID)
INNER JOIN DBA_TAB_COLUMNS TC
ON (CC.COL# = TC.COLUMN_ID
AND O.OBJECT_NAME = TC.TABLE_NAME)
WHERE 1=1
AND U.USERNAME = 'LEG'
AND O.OBJECT_TYPE = 'TABLE'
AND CC.ERRCNT <> 0;
The data sample generated as a result of the above DDL execution is as follows.
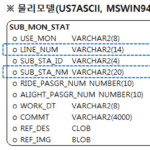
| Row# | BASE_DT | USERNAME | TABLE_NAME | COLUMN_NAME | NUMROWS | NULCNT | CNVCNT | CNVTYPE | ERRCNT | SIZERR | CNVERR | MAXSIZ | CHRSIZ |
| 1 | 20140507 | LEG | Z_TEST | VAL | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 0 |
| 2 | 20140507 | LEG | SUB_MON_STAT | LINE_NUM | 7426 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7426 | 3238 | 7426 | 38 | 0 |
| 3 | 20140507 | LEG | SUB_MON_STAT | SUB_STA_NM | 7426 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7426 | 1268 | 7426 | 54 | 0 |
| 4 | 20140507 | LEG | SUB_MON_STAT | COMMT | 7426 | 7425 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9000 | 0 |
| 5 | 20140507 | LEG | SUB_MON_STAT | REF_DES | 7426 | 7425 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3000 | 0 |
Up to this point, we have looked at the Oracle recommended character set conversion methods (CSALTER, CSSCAN). Next, we will look at the results of executing CSSCAN in the US7ASCII, KO16MSWIN949 test environment.